Virt-manager/QEMU guest
This article details the creation of a guest virtual machine (VM) running inside a QEMU hypervisor using just the virt-manager GUI tool.
For creation of the virtual machine using a CLI tool, see Libvirt/QEMU guest.
Installation
For installation of desktop user interface for management of virtual machines and containers through the libvirt library, see virt-manager.
Additional software
See libvirt for installation of virsh and virt-xml-validate.
XML editing requires app-text/xmlstarlet for extreme ease of editing complex XML files in this page.
For custom UEFI, Optional OVMF firmware is in app-emulation/virt-firmware.
User name qemu is required, defined by acct-user/qemu and evoked by sys-emulator/qemu package.
Group name qemu is required, defined by acct-group/qemu and evoked by sys-emulator/qemu package.
To connect to the SPICE server of QEMU, a GUI client like net-misc/spice-gtk is required.
Guest Linux OS requires sys-power/acpid for proper handling of guest shutdown that are initiated by the host OS using libvirt.
Configuration
Creation of a domain entails the following stages for a new domain:
- Firmware (BIOS/UEFI)
- Bootloader Manager
- OS
- Network
- Passthru devices (optional)
Creation by virt-manager
To use the GUI approach to create a virtual machine, start the Virtual Machine Management application, virt-manager.
user $virt-managerTo use the command line interface (CLI) approach only, follow this libvirt/QEMU guest wiki page.
Create a New VM
Hover the mouse over the button showing a console icon with shiny star tag (or use `File`->`New Virtual Machine` from menu bar:
How to Install
A new dialog appears that is titled "New VM" and highlighted "Create a new virtual machine" "Step 1 of 5".
Select the radio button to "Local install media".
To advance to the next step, press the "Forward" button.
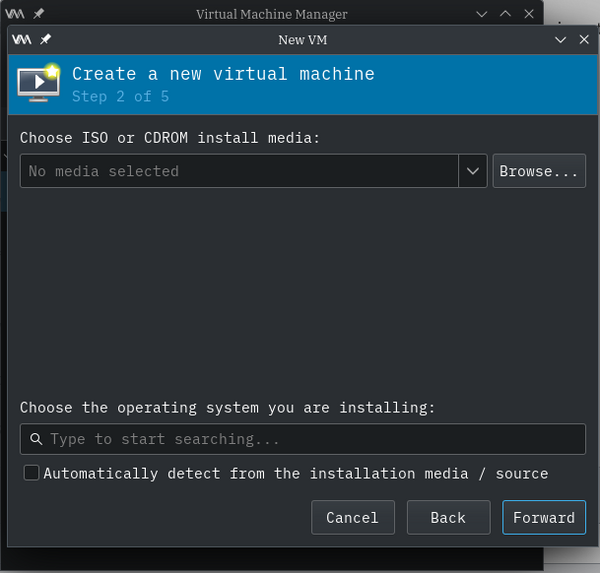
Choose Image Media
"Choose ISO or CDROM image media" "Step 2 of 5" appears.
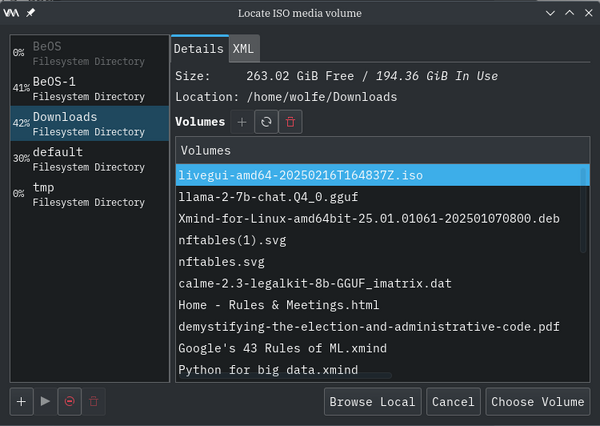
Hit the "Browse" button and find your downloaded image file: Gentoo, we hope, but any image media having this ISO 9660 CD-ROM filesystem data (DOS/MBR boot sector) will do.
Select the image file.
Click on the "Choose Volume" button.
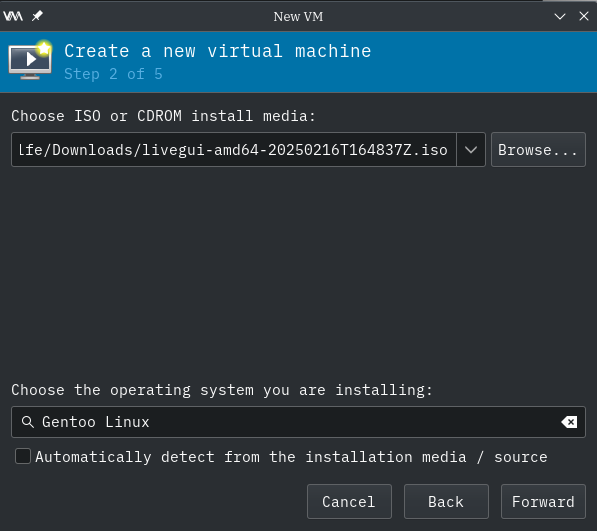
Its "Locate ISO media volume" file dialog box disappears and returns you back to the "New VM" dialog box.
Make sure that "Automatically detect from installation media / source" checkbox is DISABLED.
In the textbox titled "Choose the operating system you are installing:", enter in `gentoo` and the popup combo box appears. Mouse-click on "Gentoo Linux (gentoo)"
Press "Forward" button.
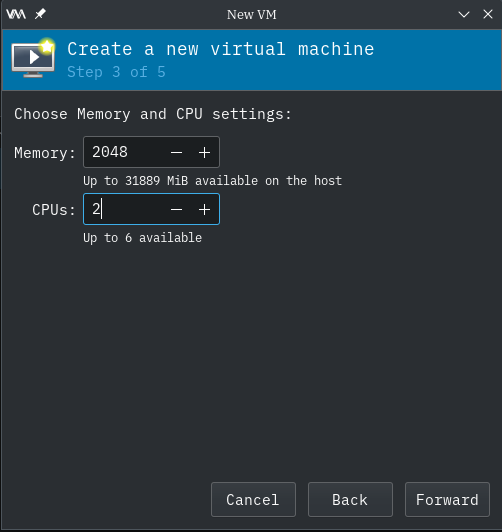
Memory and CPUs
Selecting memory and CPU is basically rocket science. Pick them as you need them. Memory can be adjusted at next run; storage size, not as easily.
Memory
In Step 3 of 5, select the amount of memory that the operating system of new virtual machine desires.
Select the number of CPUs to make available to the new virtual machine.
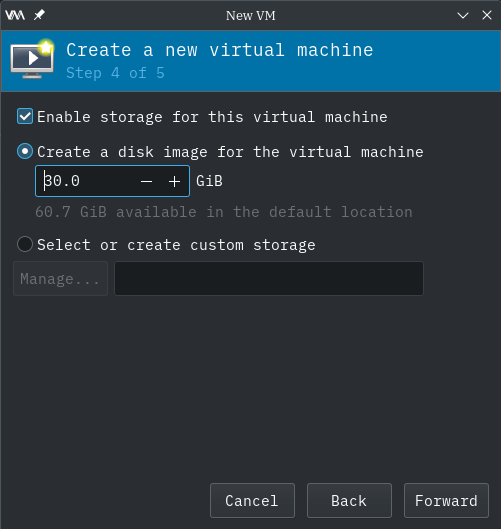
Storage
In the "New VM" dialog box, "Create a new virtual machine" and "Step 4 of 5" appears.
In the "Create a disk image for the virtual machine" textbox, increase it to the desired storage size, in gigabytes.
Press "Forward" button to continue to the next step.
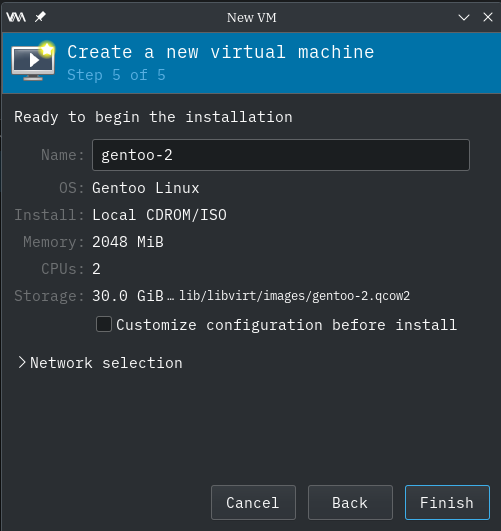
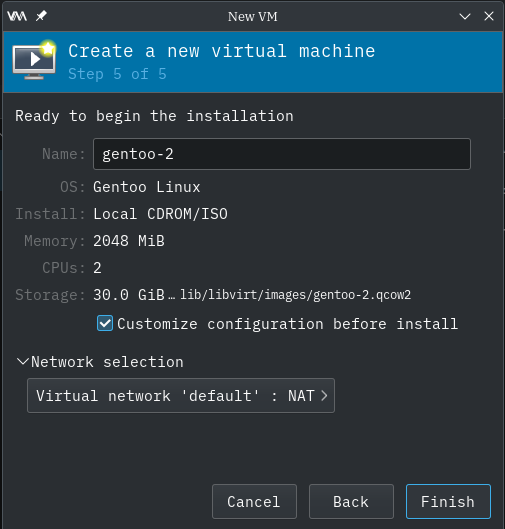
Begin Install
Step 5 of 5 window appears.
Expand the "Network Selection".
Enable the checkbox to "Customize configuration before install".
Ensure that "Virtual Network 'default': NAT" is already selected as a minimum.
Press the "Finish" button.
Tweaking VM
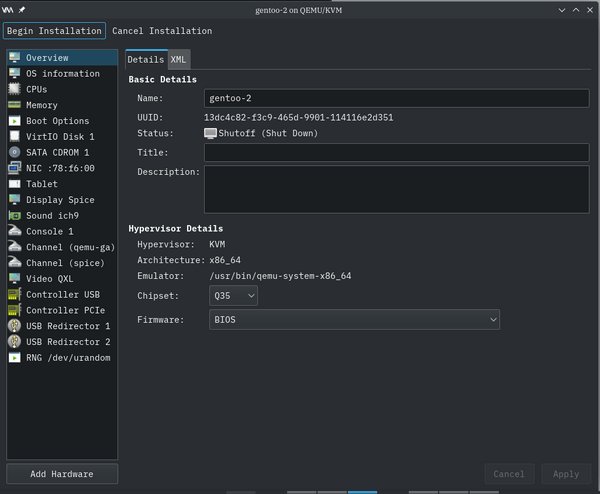
With the basic configuration largely done, you can then perform customization of this virtual machine.
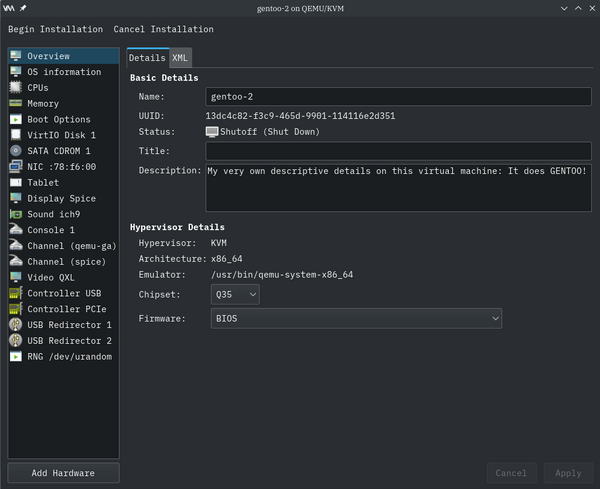
In the "Description:" textbox, add in your comment about this virtual machine.
At the top menu bar, press "Begin installation" button.
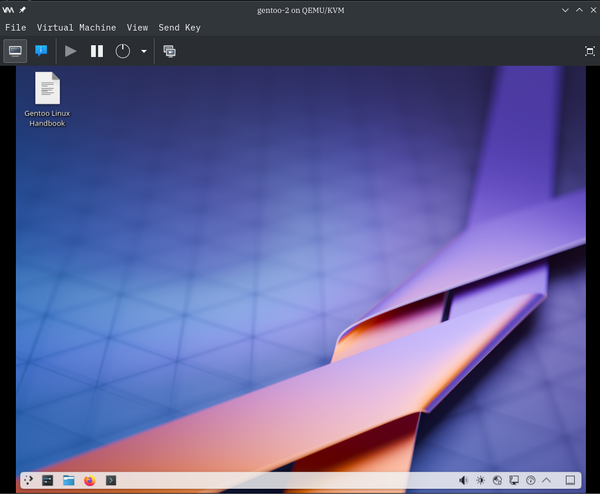
Boot Up Result
After BIOS and Linux kernel bootup, you should get a virtual machine up and running.
Usages
VM viewing
To view a virtual machine from virt-manager, execute:
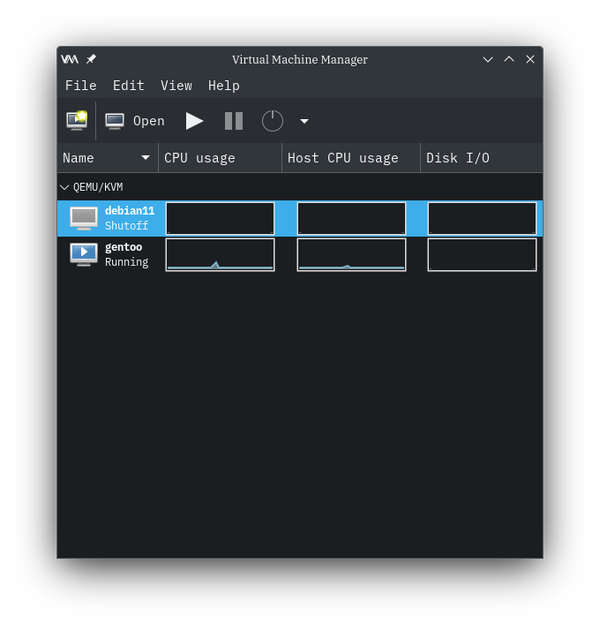
user $virt-managerA main window titled "Virtual Machine Manager" appears.
A list of domains appears at the bottom of main window.
The domain to view may be under the QEMU/KVM subcategory or under the LXC subcategory. Expand the QEMU/KVM category, if needed.
Select row of the domain that you wish to view in the main body window.
Start the virtual machine in one of two ways:
- Icons menu bar,
 menu option
menu option - Mouse-hover over domain row in the list of domain groupbox, select Open option.
Removal
To remove a domain, go to the main menu bar of virt-manager, and select the Edit menu option then Delete submenu option.
A new dialog titled "Delete Virtual Machine" appears, click on Delete button to delete the selected domain (virtual machine).
See also
- Virtualization — the concept and technique that permits running software in an environment separate from a computer operating system.
- QEMU — a generic, open-source hardware emulator and virtualization suite.
- QEMU/Front-ends — facilitate VM management and use
- Libvirt — a virtualization management toolkit
- Libvirt/QEMU_networking — details the setup of Gentoo networking by Libvirt for use by guest containers and QEMU-based virtual machines.
- Libvirt/QEMU_guest — creation of a guest domain (virtual machine, VM), running inside a QEMU hypervisor, using tools found in libvirt package.
- Virt-manager — lightweight GUI application designed for managing virtual machines and containers via the libvirt API.
- QEMU/Linux guest — describes the setup of a Gentoo Linux guest in QEMU using Gentoo bootable media.