Firefox
Firefox is Mozilla's web browser.
The Firefox browser should not be confused with Firefox OS, a discontinued operating system. There was an "unbranded" version of Mozilla's Firefox called "Aurora".
Installation
USE flags
USE flags for www-client/firefox Firefox Web Browser
+X
|
Add support for X11 |
+clang
|
Use Clang compiler instead of GCC |
+gmp-autoupdate
|
Allow Gecko Media Plugins (binary blobs) to be automatically downloaded and kept up-to-date in user profiles |
+jumbo-build
|
Enable unified build - combines source files to speed up build process, but requires more memory |
+system-av1
|
Use the system-wide media-libs/dav1d and media-libs/libaom library instead of bundled |
+system-harfbuzz
|
Use the system-wide media-libs/harfbuzz instead of bundled and media-gfx/graphite2 in most cases |
+system-icu
|
Use the system-wide dev-libs/icu instead of bundled |
+system-jpeg
|
Use the system-wide media-libs/libjpeg-turbo instead of bundled |
+system-libevent
|
Use the system-wide dev-libs/libevent instead of bundled |
+system-libvpx
|
Use the system-wide media-libs/libvpx instead of bundled |
+system-webp
|
Use the system-wide media-libs/libwebp instead of bundled |
+telemetry
|
Send anonymized usage information to upstream so they can better understand our users |
dbus
|
Enable dbus support for anything that needs it (gpsd, gnomemeeting, etc) |
debug
|
Enable extra debug codepaths, like asserts and extra output. If you want to get meaningful backtraces see https://wiki.gentoo.org/wiki/Project:Quality_Assurance/Backtraces |
eme-free
|
Disable EME (DRM plugin) capability at build time |
gnome-shell
|
Integrate with gnome-base/gnome-shell search |
hardened
|
Activate default security enhancements for toolchain (gcc, glibc, binutils) |
hwaccel
|
Force-enable hardware-accelerated rendering (Mozilla bug 594876) |
jack
|
Add support for the JACK Audio Connection Kit |
libproxy
|
Enable libproxy support |
openh264
|
Use media-libs/openh264 for H264 support instead of downloading binary blob from Mozilla at runtime |
pgo
|
Add support for profile-guided optimization for faster binaries - this option will double the compile time |
pulseaudio
|
Add sound server support via media-libs/libpulse (may be PulseAudio or Pipewire, or apulse if installed) |
selinux
|
!!internal use only!! Security Enhanced Linux support, this must be set by the selinux profile or breakage will occur |
sndio
|
Enable support for the media-sound/sndio backend |
system-png
|
Use the system-wide media-libs/libpng instead of bundled (requires APNG patches) |
valgrind
|
Enable annotations for accuracy. May slow down runtime slightly. Safe to use even if not currently using dev-debug/valgrind |
wasm-sandbox
|
Sandbox certain third-party libraries through WebAssembly using RLBox |
wayland
|
Enable dev-libs/wayland backend |
wifi
|
Enable necko-wifi for NetworkManager integration, and access point MAC address scanning for better precision with opt-in geolocation services |
The above list of USE flag is not comprehensive. Use equery (part of app-portage/gentoolkit) for a full list:
user $equery uses www-client/firefoxUsing GCC rather than Clang to compile Firefox makes Firefox have slower performance because Firefox has Rust code. Because both Rust and Clang uses LLVM, Clang is able to make better optimizations than GCC (This is subject to change with the GCC Rust).
Note that USE="-pulseaudio" will select the ALSA audio back-end.
LTO
If LTO isn't enabled globally, it can be enabled just for Firefox via an env file,
/etc/portage/env/lto.conflto.confCFLAGS="-march=native -O2 -pipe -flto"
CXXFLAGS="${CFLAGS}"
Then make Firefox use the newly created env file with:
/etc/portage/package.env/firefoxFirefox lto config examplewww-client/firefox lto.conf
-flto=auto, -flto=thin etc will also be detected and LTO enabled for Firefox.
Enabling LTO for Firefox is recommended even when the rest of the system isn't LTO'd, because the performance increase from LTO itself in the Firefox browser is remarkable.
- https://documentation.suse.com/sbp/devel-tools/html/SBP-GCC-11/index.html#sec-gcc11-firefox
- https://documentation.suse.com/sbp/devel-tools/html/SBP-GCC-10/index.html#sec-gcc10-firefox
Emerge
Firefox takes a relatively long time to compile. Unless there is a specific reason not to (such as the need for non default USE flags), use the "-bin" version to save time!
Binary package (firefox-bin)
Emerging the source version of Firefox can be a long process, so there is a pre-compiled (binary) version in the Gentoo ebuild repository. To emerge the Firefox binary:
root #emerge --ask www-client/firefox-binUsing the pre-compiled www-client/firefox-bin package means that almost all of the USE flags in the list above cannot be set: setting these flags while using this package will not alter the binary.
From source
To install Firefox from source:
root #emerge --ask www-client/firefoxThis will install Firefox Extended Support Release (ESR) on a stable branch Gentoo system (or Firefox "Rapid release" if ~amd64 keyword is selected).
For information about Firefox releases, see choosing a Firefox update channel.
Specify a slot
This will explain how to select a Firefox package from a specific slot.
To select a release irrespective of keywords, subscribe to a slot:
root #emerge --ask www-client/firefox:esrOr:
root #emerge --ask www-client/firefox:rapidThis will add the package from a specific slot to the selected set (/var/lib/portage/world). Read more about the motivation of slotting.
If a slot for Firefox has been previously selected, start by using
--deselect to remove the entry from the world file:
root #emerge --deselect www-client/firefox:esr
root #emerge -av www-client/firefox:rapidConfiguration
Running under Wayland
In www-client/firefox and www-client/firefox-bin, Wayland will be enabled by default if the
wayland USE flag is set. These instructions are kept in case that still fails.Since Firefox 65, it is possible to run Firefox natively under Wayland by launching it with the GDK_BACKEND=wayland environment variable set after having emerged Firefox with the USE flag wayland enabled. From a terminal:
user $GDK_BACKEND="wayland" firefoxAlso, make sure that the generic Wayland environment variables XDG_RUNTIME_DIR, WAYLAND_DISPLAY, and XDG_SESSION_TYPE are exported correctly to ensure that GDK can communicate with the compositor.
To set Firefox to always open using the Wayland backend, set the following environment variable in the user's shell. Bash is the default user shell on Gentoo systems:
~/.bash_profile# Enable Wayland support for Mozilla Firefox
export MOZ_ENABLE_WAYLAND=1
Enabling multitouch
Xinput2 scrolling
This brings touch scrolling and multitouch support for Firefox:
MOZ_USE_XINPUT2 environment variable has to be set to a value of 1 in /etc/env.d/80firefox, or just before launching firefox in a shell. for example:
user $MOZ_USE_XINPUT2="1" firefoxThis also eliminates the predefined scroll step size for touchpad scrolling! All scrolling will be really smooth.
Wacom tablets/touchscreens may need extra configuration so they emit true touch events for X.
Multitouch zoom
This only works when the multitouch events reach Firefox, therefore the Xinput2 activation above has to be done first.
| Description | about:config option | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Multitouch activation | gestures.enable_single_finger_input
|
False
|
| Zoom in | browser.gesture.pinch.in
|
cmd_fullZoomReduce
|
| Zoom out | browser.gesture.pinch.out
|
cmd_fullZoomEnlarge
|
Middle mouse scroll (autoscroll)
Traditionally in Linux, the middle mouse button is used to paste the currently selected (highlighted) text into a text field. On Windows systems, the middle mouse button in Firefox is used for click-and-drag scrolling up and down the page. This functionality can be enabled in Firefox by opening about:config and setting the following value[1]:
general.autoScroll = true
Middle click-and-drag scrolling should now be enabled.
Although not necessary, sometimes it is desirable to disable all other middle-click functionality within Firefox when using click-and-drag scrolling. Open about:config and set the following values to disable middle-click functionality:
middlemouse.contentLoadURL = falsemiddlemouse.openNewWindow = falsemiddlemouse.paste = false
Bigger scrolling regions for Up/Down
PageUp/PageDown scroll for a page, Up/Down scroll for a line, many will benefit if Up/Down would scroll for a few lines:
| Description | about:config option | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Vertical scroll distance, not for mouse (default is 3) | toolkit.scrollbox.verticalScrollDistance
|
30
|
To increase scrolling size for a mouse also:
| Description | about:config option | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Vertical scroll distance, for mouse and keyboard (default is 1) | mousewheel.min_line_scroll_amount
|
N
|
Threads
Firefox >= 54 < 66 has 4 threads enabled by default[2]. Firefox >= 97 also has fission site isolation enabled by default[3]. Adjusting threads now does nothing with fission enabled and the UI option for changing the number of threads is also gone when fission is enabled[4], Number of process per-site[5] can be adjusted by modifying the corresponding option in the about:config interface:
| Description | about:config option | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Increase the threads | dom.ipc.processCount
|
N
|
| Increase the Number of process per-site | dom.ipc.processCount.webisolated
|
N
|
Where N is an integer number.
Audio backend
Firefox's cubeb audio library supports a number of different backends.[6][7] A backend can be specified by creating and setting media.cubeb.backend in about:config. A selection of available backends is listed below; the 'Value' column indicates the appropriate value for media.cubeb.backend, and the 'Status' column indicates the current level of support for that backend:
- Tier-1: Actively maintained. Should have CI coverage. Critical for Firefox.
- Tier-2: Actively maintained by contributors. CI coverage appreciated.
- Tier-3: Maintainers/patches accepted. Status unclear.
- Tier-4: Deprecated, obsolete. Scheduled to be removed.
| Description | Status | Value |
|---|---|---|
| ALSA | Tier-3 | alsa
|
| JACK | Tier-3 | jack
|
| OSS | Tier-2 | oss
|
| PulseAudio (C) | Tier-4 | pulse
|
| PulseAudio (Rust) | Tier-1 | pulse-rust
|
| sndio | Tier-2 | sndio
|
Obviously, to use Firefox with JACK, www-client/firefox should be installed with the USE flag jack enabled.
Disabling percent-encoding
Normally, URLs that are copied from the address bar get percent-encoded. This may cause an annoyance when certain non-Latin symbols (such as Cyrillic) get encoded, as they become unreadable to humans.
To disable percent-encoding when copying from the address bar, set the about:config option network.standard-url.escape-utf8 to false.
Unfortunately Firefox does not support non-Latin symbols in anchors, those remain encoded (not percent-encoded, though).
Disable enforced digital signatures verification in Firefox >=48
This concerns mandatory add-ons signature in Firefox and can lead to security issues.
Method 1
Create this file:
/usr/lib/firefox/config.js//
try {
Components.utils.import("resource://gre/modules/addons/XPIProvider.jsm", {})
.eval("SIGNED_TYPES.clear()");
}
catch(ex) {}
END
Then insert this:
/usr/lib/firefox/defaults/pref/channel-prefs.jspref("general.config.obscure_value", 0);
pref("general.config.filename", "config.js");
Method 2
https://gist.github.com/anonymous/a661949550a26b9522f79095f8ae2d94
Method 3
This patch works for both firefox 49 and firefox 51, and seems to be robust to changes.
/etc/portage/patches/www-client/firefox/no-signature-force-check.patch--- a/build/mozconfig.common.override 2017-02-06 14:26:05.891721140 +0900
+++ b/build/mozconfig.common.override 2017-02-06 14:25:41.115763755 +0900
@@ -9,3 +9,4 @@
# to override anything done previously.
#
# The common expected usage is for try builds with nondefault options.
+MOZ_REQUIRE_SIGNING=0
The following patch also works for firefox 49.
/etc/portage/patches/www-client/firefox-49.0/no-signature-force-check.patchdiff --git a/browser/confvars.sh.old b/browser/confvars.sh
index 7637236..2264bf5 100755
--- a/browser/confvars.sh.old
+++ b/browser/confvars.sh
@@ -27,7 +27,16 @@ fi
# Enable building ./signmar and running libmar signature tests
MOZ_ENABLE_SIGNMAR=1
-MOZ_SAFE_BROWSING=1
+# Disable 'safe' browsing
+MOZ_SAFE_BROWSING=0
+# Disable checking that add-ons are signed by the trusted root
+# https://github.com/mozilla/positron/blob/master/build/mozconfig.common
+MOZ_ADDON_SIGNING=0
+# Disable enforcing that add-ons are signed by the trusted root
+MOZ_REQUIRE_SIGNING=0
+# https://dxr.mozilla.org/mozilla-central/rev/5cf4d2f7f2f2b3df2f1edd31b8bdce7882f3875c/browser/confvars.sh
+# https://dxr.mozilla.org/mozilla-central/source/browser/confvars.sh
+
MOZ_APP_VERSION=$FIREFOX_VERSION
MOZ_APP_VERSION_DISPLAY=$FIREFOX_VERSION_DISPLAY
MOZ_EXTENSIONS_DEFAULT=" gio"
Then set xpinstall.signatures.required to false.
Special URLs
Firefox includes a few dozen special URLs that can be helpful in determining more information about various Firefox settings. These URLs can be entered into the Super Bar (via copy and paste) to view the special pages. A few of the more significant ones include:
about:addons- Page for managing extensions.about:buildconfig- Page containing build information about the currently running version of Firefox. Use this page to check what compiler flags were set during Firefox's build.about:cache- Information about the Network Cache Storage Service.about:config- Modify internal browser settings and preferences.about:memory- Measure and show memory reports, free memory, etc.about:networking- Analyze current network information such as HTTP, socket, and DNS connections.about:plugins- List installed plugins such as Widevine Content Decryption Module (DRM software).about:support- A page containing technical information that might be useful when trying to solve a problem. Includes information on WebGL, Window Protocol (X11 or Wayland), and compositing graphics backends.about:telemetry
Finally, about:about will display the whole list of Firefox' “about” pages. A description for each page is available at Firefox and the "about" protocol.
See also Firefox chrome:// document URLs.
XDG integration
In order to make Firefox use XDG file associations set Content Type's Action to /usr/bin/xdg-open
To ensure Firefox is being used by other applications for handling HTTP and HTTPS links, run the following command:
user $xdg-mime default firefox.desktop x-scheme-handler/http x-scheme-handler/https text/htmlRunning under KDE
Firefox is built with GTK, and by default will use the GTK file picker. To enable the KDE file picker, install kde-plasma/xdg-desktop-portal-kde, which is installed by default if kde-plasma/plasma-meta is installed. After that set widget.use-xdg-desktop-portal to true and widget.use-xdg-desktop-portal.file-picker to 1 in about:config.
Enabling color management
See the dedicated Color management section.
Disabling Privacy-Preserving Attribution
To disable the Privacy-Preserving Attribution API added in version 128,[8][9][10] set dom.private-attribution.submission.enabled to false.[11] Or compile Firefox with -telemetry use flag.
Disabling AI Chatbots
To disable the AI Chatbot sidebar feature added since version 130,[12][13] set browser.ml.chat.enabled to false.[14]
Security
Running in sandbox
It is highly recommended to run your browser inside a sandbox, to limit its access to e.g. your home directory. There are many alternative sandboxing applications with this functionality to choose from.
Please see Simple sandbox for suggestions on sandboxing Firefox.
SSL/TLS security enhancements
Some about:config SSL/TLS security options which are not defaults (as of Firefox 52.2.0) that increase the security of HTTPS connections are listed below. Two of them rarely break access to websites.
| Description | about:config option | Value |
|---|---|---|
Minimal TLS version set to 1.1. Default is 1 meaning TLS 1.0, unsecure. May break access to some badly configured websites.
|
security.tls.version.min
|
2
|
| Avoiding old SSL/TLS version. May break access to some badly configured websites. | security.ssl.require_safe_negotiation
|
true
|
| Inform user about insecure SSL/TLS negociation (broken padlock). | security.ssl.treat_unsafe_negotiation_as_broken
|
true
|
| Require Online Certificate Status Protocol. Introduces some latency. | security.OCSP.require
|
true
|
| Strict Certificate Pinning. | security.cert_pinning.enforcement_level
|
2
|
| Don't use DES. | security.ssl3.rsa_des_ede3_sha
|
false
|
| Don't use RC4. | security.ssl3.rsa_rc4_128_md5 (if present)
|
false
|
| Don't use RC4. | security.ssl3.rsa_rc4_128_sha (if present)
|
false
|
| No Google SSL False Start. | security.ssl.enable_false_start
|
false
|
Safer browsing with add-ons
Many users are concerned about their privacy (tracking, bubbling, targeting, etc) while web browsing. Installing Add-ons can aid in adding an extra level of privacy to their browsing.
The add-on menu can be accessed by navigating the following menus: Hamburger button (top right under the X) → Add-ons
Occasionally certain add-ons will use key press event listeners for input from the user. FireFox's "Search for text when I start typing" feature can conflict with key press event listeners used by add-ons. This feature can be disabled by navigating to Hamburger button (top right under the X) → Preferences → Browsing and unchecking the "Search for text when I start typing" option.
uBlock Origin
uBlock Origin is "a wide-spectrum content blocker with CPU and memory efficiency as a primary feature".[15] It enables 5 filter lists by default and others are available.
- Mozilla Add-ons page: https://addons.mozilla.org/en/firefox/addon/ublock-origin/
- GitHub: https://github.com/gorhill/uBlock
- Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/UBlock
AdNauseam
AdNauseam provides the same functionality as uBlock Origin but also "quietly clicks on every blocked ad"[16] with the goal of resisting ad network tracking efforts through obfuscation. Some research in 2021 showed it to be effective for individual users.[17]
- Mozilla Add-ons page: https://addons.mozilla.org/en-GB/firefox/addon/adnauseam/
- Homepage: https://adnauseam.io/
- GitHub: https://github.com/dhowe/AdNauseam
LibRedirect
A web extension that redirects YouTube, Twitter, TikTok, and other websites to alternative privacy friendly frontends. The extension is very customizable, including the possibility of enabling/disabling redirection per service category.
- Mozilla Add-ons page: https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/libredirect/
- Homepage: https://libredirect.github.io/
Facebook Container
Facebook is able to track the activity of both loged-in and logged-out users through the presence of widgets such as a "like"/"share" button on a website. This add-on, created by Mozilla themselves, utilizes Firefox container tabs to isolate Facebook (and related sites such as Instagram) from the rest of your web sessions. When installed, accessing any Facebook sites will automatically open the page in a Facebook container tab. Accessing a non-Facebook site from within the container will automatically open the page in a tab outside of the container. Additionally, it disables the Facebook widgets outside of the Facebook container.
- Mozilla Add-ons page: https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/facebook-container/
- GitHub: https://github.com/mozilla/contain-facebook
Installing the Facebook Container add-on will automatically log the user out of Facebook, close any open Facebook tabs, and delete all Facebook cookies. It also enables the "container tabs" feature in Firefox. This add-on is disabled during private browsing.
NoScript
NoScript blocks JavaScript that is normally enabled by default. It can keep users safe and speed up web browsing.
- Mozilla Add-ons page: https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/noscript/
- Homepage: https://noscript.net/
Video speed controller
Using an HTML5 video speed controller can be helpful in accelerating the playback rate of HTML 5 video. This is useful when binging video content on sites that do not offer increases in video playback speed (such as Amazon Prime Video or Netflix).
- Mozilla Add-ons page: https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/videospeed/
- GitHub: https://github.com/codebicycle/videospeed
Behind The Overlay
Some websites use modal overlays to display pop-ups, such that manually blocking the overlay with an add-on like uBlock Origin causes the page to become unscrollable. This add-on provides a one-click solution for bypassing such cases without the need to tinker with custom filtering rules.
- Mozilla Add-ons page: https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/behind_the_overlay/
- GitHub: https://github.com/NicolaeNMV/BehindTheOverlay
Policies
Custom policies can be configured in Firefox, which is particularly useful in cases where Firefox is set up for an organization or end users. However, it can also be beneficial to block specific content for personal use. [18]
The procedure may vary if the binary has been utilized. For this particular procedure, it is assumed that Firefox has been compiled on the system. To configure custom policies in this scenario, it is necessary to create a JSON file in the following directory:
/etc/firefox/policies/policies.json
The JSON file must meet the following structure:
/etc/firefox/policies/policies.json{
"policies": {
"policy_name": policy_value
}
}
As an example, creating a policy that blocks about:config and all URLs except for the Gentoo page and its subpages would require the following contents in the corresponding JSON file:
/etc/firefox/policies/policies.json{
"policies": {
"BlockAboutConfig": true,
"WebsiteFilter": {
"Block": ["<all_urls>"],
"Exceptions": ["https://www.gentoo.org/*"]
}
}
}
It is important to ensure, that the
policies.json is not writable by non-admin users, to prevent overwriting of the policies by users, which would defeat the purpose of policies! The chown and chmod commands can be used to change ownership and rights if for any reason the file should be writable by non-admin users.The success of the configuration can and should always be verified by checking the special page about:policies. This page also contains documentation and examples for other policy options. A complete list of policies can also be found in the policy templates provided by Mozilla on GitHub.
It is recommended to carefully study the list, especially when the configuration is for other users. An approach of first blocking everything and then allowing specific desired pages is always preferable, as it reduces the likelihood of overlooking pages. Special pages and protocols (such as the file:// protocol)[19] that are not desired to be used, should also be considered to be blocked to prevent abuse of the security policies.
Local certificates
Although Firefox uses the NSS library for handling the secure communications, it doesn't use the ~/.pki/nssdb/ location, nor the system-wide CA certificate list in /etc/ssl/certs/. Instead, it uses its own list, stored in the file cert9.db in each Firefox profile directory (e.g. ~/.mozilla/firefox/xxxxxxxx.default/. The cert9.db file is an SQLite database; previously, a BerkeleyDB database was used, and the relevant file was cert8.db.
To list Firefox's intermediate CA certificates, use certutil(1) (provided by dev-libs/nss) and installed as a dependency of Firefox and other packages):
user $certutil -L -d ~/.mozilla/firefox/*.default/Certificate Nickname Trust Attributes
SSL,S/MIME,JAR/XPI
DigiCert High Assurance CA-3 ,,
DigiCert Secure Server CA ,,
InCommon Server CA ,,
...
Local certificates should be installed in /usr/local/share/ca-certificates, and have the extension .crt (instead of e.g. .pem), as the extension checked by the update-ca-certificates script.
To add the certificate to the certificate list for a particular profile:
- In Firefox, select Edit > Settings > Privacy & Security. Scroll to the "Certificates" section, then select the "View certificates" button; this will open the "Certificate Manager" dialog. Select the "Import" button.
- On the command line, use the certutil(1) utility:
user $certutil -d ~/.mozilla/firefox/xxxxxxxx.default/ -A -n cert-nickname -i /usr/local/share/ca-certificates/my-cert.crt -t "CT,,"To add a certificate to the certificate list for all profiles, add the following to the /etc/firefox/policies/policies.json file (as described in the #Policies section), creating it if necessary:
/etc/firefox/policies/policies.jsonFireFox certificates{
"policies": {
"DisableAppUpdate": true,
"Certificates": {
"ImportEnterpriseRoots": true,
"Install": [
"/usr/local/share/ca-certificates/my-cert.crt"
]
}
}
}
Hardware acceleration
Enable the hwaccel USE flag for Firefox to get correct about:config options. Firefox >116 will also install helper binaries, like vaapitest. This flag may cause Firefox to crash and is not necessary for hardware acceleration. If so, try the options below.
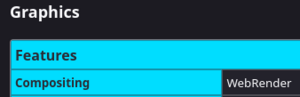
Verify that web render hardware acceleration is working by going to about:support#graphics and searching for Compositing. A value of WebRender means hardware acceleration is enabled, while WebRender (software) means it's not. If you have installed the correct video card drivers but WebRender is still using software rendering, try setting gfx.webrender.all to true in about:config.
Hardware accelerated video decoding status can also be checked on the about:support#graphics page. Search for HARDWARE_VIDEO_DECODING. Available means it's working. If video decoding is disabled, you may need to setup VA-API or VDPAU drivers.
Since 116, the wayland USE flag isn't needed to get hardware acceleration on supported cards for Rapid. For ESR, 115 needs the hwcaccel wayland USE flags enabled to get hardware acceleration. X and wayland can be enabled simultaneously. > 116 was fixed to have hardware acceleration without wayland support.
| AMD | Intel | Nvidia | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESR | Should 'just work' if the card is supported. > 116 will have more cards supported than 115. | Should work if the card is supported (> Haswell). | Install media-libs/nvidia-vaapi-driver and check its upstream documentation. Currently, nouveau does not support hardware acceleration in Firefox. | |||||||||||||||||||
| Rapid | Should work if the card is supported. | Should work if the card is supported (> Haswell). | Install media-libs/nvidia-vaapi-driver and check its upstream documentation. Currently, nouveau does not support hardware acceleration in Firefox. | |||||||||||||||||||
Troubleshooting
Disable hardware acceleration
While disabling the hwaccel USE flag will get rid of the required about:config options, these can be enabled manually regardless of the USE flag status. To disable hardware acceleration, edit about:config with media.hardware-video-decoding.enabled set to false.
Green artifacts on a video only with hardware acceleration
Try setting media.navigator.mediadatadecoder_vpx_enabled to false in about:config.
Hardware acceleration not working
Make sure media-video/libva-utils and sys-apps/pciutils are installed. Make sure vaapi works outside Firefox first with vainfo program. Try a different program to confirm vaapi works there, e.g. mpv --hwdec=vaapi.
Debug the issue with MOZ_LOG="PlatformDecoderModule:5" firefox.
Hardware acceleration not working within a sandbox
When using an external sandbox application, such as sys-apps/bubblewrap or sys-apps/firejail, make sure that hardware acceleration works outside the sandboxing. Hardware acceleration will require more ro access permissions from /dev and /sys.
Troubleshooting
No video with supported format and MIME type found
In about:config try to toggle media.rdd-process.enabled (default is true).
Audio
Lack of sound (www-client/firefox-bin)
www-client/firefox-bin expects PulseAudio. ALSA-only systems might work around this limitation by using media-sound/apulse. For this to work, modify Firefox sandbox settings by going to about:config and adding /dev/snd/ (note the trailing slash) to the security.sandbox.content.write_path_whitelist option.
If storing ALSA settings in $HOME, also, be sure to add $HOME/.asoundrc to the security.sandbox.content.write_path_whitelist option. Whitelist path could be separated by comma.
Since around Firefox 58 there is additional modification needed to work around seccomp sandbox: security.sandbox.content.syscall_whitelist = 16
It is now possible to go ahead and create alias for running Firefox through apulse:
user $alias firefox='apulse firefox-bin'Lack of sound when using PipeWire (www-client/firefox)
Problem: System sound is working properly, but Firefox itself is unable to provide sound playback.
Cause: The www-client/firefox package has support for three audio backends: ALSA, JACK and PulseAudio. With PipeWire becoming the standard audio backend on Linux, support for ALSA (via the alsa USE flag) or PulseAudio (via the pulseaudio USE flag) may not be enabled by the target desktop profile. The default audio backend for Firefox can be checked under about:support#media under Audio Backend:
Solution: Enable the pulseaudio USE flag for Firefox and then recompile Firefox. Be sure to follow the steps detailed in the PipeWire article to setup pipewire-alsa.
Sound crackling when using Pipewire or JACK (www-client/firefox)
Problem: System sound is crackling.
Cause: The www-client/firefox package has support for two audio backends: JACK and PulseAudio. When using Pipewire, see Arch Linux forum post on the issue. When using JACK, in the Configure dialog of media-sound/qjackctl or media-sound/cadence, to set Buffer Size: 1024 and Periods/Buffer: 8 works fine for me.
Crashes
If Firefox crashes for no apparent reason every few minutes with an error message like ABORT: X_GLXDestroyContext: GLXBadContext; 15 requests ago it might help to add the Firefox user(s) to the video group:
root #gpasswd -a <username> videoGraphics/video
Green video screen (YouTube)
If disabling (graphics) acceleration in settings does not work, disabling the equivalent options under about:config like layers.acceleration.force-enabled (85.0) might.
Screen tearing / stuttering smooth scrolling
Build www-client/firefox with the hwaccel USE flag , then check the Compositing value of the about:support#graphics table for WebRender.
This solution does not work with www-client/firefox-bin because the USE flag is not available.
Systems with Wayland support should not have issues with screen tearing.
If WebRender is enabled, then the problem could be with the video drivers. For example about Intel.
gtk+:3 pulls in D-Bus
Since version ≥53.0, Firefox has dropped gtk+:2 support urging Larry to use gtk+:3. This, however, by default, pulls-in dependencies like D-Bus unconditionally. This can be avoided by using a patch from BSD available in bug #669234 or the mv overlay.
Please note that, when running Firefox under native Wayland (i.e. not using XWayland), Firefox will implicitly try to use D-Bus to enable its remote control feature and crash, likely with a segfault, due to the lack of D-Bus. Thus, it is necessary to invoke Firefox with the --no-remote command-line argument or MOZ_NO_REMOTE environment variable set (to anything).
KDE Plasma Integration: failed to connect to the native host
If using www-client/firefox-bin, plasma integration might not work with default install due to org.kde.plasma.browser_integration.json installed in an unexpected directory (/usr/lib64/mozilla instead of /usr/lib/mozilla). See bug bug #687736 for details.
As a work around, creating a symlink will work:
root #ln -s /usr/lib64/mozilla /usr/lib/mozillaSpeech dispatcher library missing
Some webpages may result in Firefox giving a notice that "You can’t use speech synthesis because the Speech Dispatcher library is missing.”[20] To fix this,
root #emerge --ask app-accessibility/speech-dispatcherWayland
Determine if Firefox is running the Wayland protocol backend
To determine if Firefox is running with the Wayland protocol as a backend, check about:support#graphics table for the Window Protocol value. "wayland" will be displayed when running on the Wayland protocol. Other possible values include Xwayland and x11.
"Failed to load cursor theme Adwaita" in Wayland
This happens because Firefox attempts to use /usr/local/share/icons. [21] See the reference above for the fix.
Touchpad scrolling feels too fast on Wayland
Change the option apz.gtk.pangesture.delta_mode from 0 to 2. Further tweaks are discussed in this Mozilla bugtracker thread.
Windows decorations missing in Fluxbox since FF-91.3.0
- https://forums.gentoo.org/viewtopic-t-1141870.html Solved in 91.9.0esr and back with 102.3.0esr (64-bit)
Once in a while this happens. What might then help is to restart fluxbox with the menu.
Troubleshooting tips
If the problem cannot be clearly identified and the search engine search also does not provide a helpful solution, one good starting point for further investigation could be the special page about:support. This page contains, like mentioned in the special pages section, further technical information, along with more special pages like about:memory and others. This pages can be used for a more detailed investigation of the problem. The page can also be used to copy the raw technical data to obtain support. In this case, it is important to ensure that the copied content do not contain information which should not be published - if asking in a forum for assistance for example.
In the following steps it is assumed that Firefox was compiled on the system. If the binary was utilized, it is necessary to replace firefox with firefox-bin in the commands mentioned bellow. Whether the same applies to directories should be verified. Additionally, some of the following steps require a running graphical environment.
If Firefox is used only in headless mode on a system without any graphical environment, the following procedure might not work or not work as expected.
Safe mode
Starting Firefox in safe mode temporarily disables add-ons, hardware acceleration and WebGL, window and sidebar size along with other position settings, userChrome and userContent customizations, and the JavaScript JIT compiler.[22] This can help to determine if a problem is related to any of the aforementioned components and whether it can be resolved by removing custom settings in those sections.
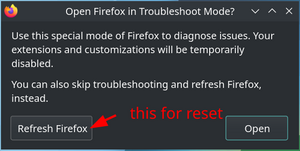
To start Firefox in safe mode, the Troubleshooting Mode on the special page about:support can be used.[23] This can also be achieved by using the CLI. This is particularly useful when the about:support page is not accessible, such as when Firefox does not even start:
user $firefox --safe-modeIf prompted to choose between a refresh or proceeding with the troubleshooting mode, it is recommended to test first whether the troubleshooting mode solves the problem. This can be done by conforming with the "Open" option.
If the problem does not persist in safe mode, than it is probably related to hardware acceleration, custom themes, or to custom extensions. To deactivate these elements step-by-step and further narrow down the problem, this guide by Mozilla can be followed.
If the problem was not caused by themes or extensions, but rather by hardware acceleration, it is recommended to review the Gentoo Hardware Acceleration Guide, and to see if the issue can be resolved using the suggested steps there. This ensures that hardware acceleration was configured properly.
If the problem was caused by custom themes, extensions, or other custom settings within the following removal scope, a simple refresh may solve the problem. Refreshing Firefox will remove these settings and reset them to their default values:
- Extensions and themes
- website permissions
- Modified preferences
- Added search engines
- DOM storage
- Security certificates and device settings
- Download actions
- Toolbar customization and user styles (This also removes userChrome and/or userContent CSS files if they were created. If this custom files were created, a backup of these will be required before proceeding to prevent data loss)[24].
A refresh can be performed either via the special page about:support and by searching the "Refresh Firefox" option or via the command line interface. To refresh via CLI:
user $firefox --safe-modeIf prompted, select "Refresh Firefox". This will not reset bookmarks, history, passwords, cookies, auto fill, and the personal directory[25].
Startup cache
If the problems are related to startup issues, like slow loading times of the Firefox application after launch or immediate crashes after startup, a broken startup cache could be one of the possible problems. To test if the startup cache causes the undesired behavior it is possible to simply clear the startup cache. One way of doing so, is to search the associated option in the about:support page. Please note that clearing the cache via about:support do not provide a possibility to revert the cleared cache. However, the startup cache can also be cleared manually with a backup option.
The Firefox startup cache is typically located in the directory: ~/.cache/mozilla/firefox
Please be aware that the mozilla folder may also contain the caches from other Mozilla applications, like Thunderbird. To reset the Firefox startup cache, it is required to rename the folder, so Firefox can create a new clean startup cache on the next startup:
user $cd ~/.cache/mozillauser $mv firefox firefox_oldIf this solves the problem and the old cache is not needed anymore, it can be deleted. If the problem was not caused by the startup cache, the changes can be easily reverted:
user $cd ~/.cache/mozilla
user $rm -r firefox
user $mv firefox_old firefox
Reset profile
This solution works with important user related profile settings. Special attention is required to avoid data loss!
Firefox stores personal information such as bookmarks, passwords and user preferences on a separate location. To quick check if the problems are caused through profile misconfiguration, it is possible to use the same approach as in clearing the startup cache. Attention is required while performing this tasks, because they usually contain user related data, like password and alike.
To find the path of the profile location the about:support page can be used.
For instance, a path example could be: /home/username/.mozilla/firefox/ntgqave6.default-esr-1679659083216
If the support page is not accessible, the usual storage location is: ~/.mozilla/firefox
To quick check profile related issues:
user $cd ~/.mozilla
user $mv firefox firefox_bak
This removes all existing profiles and Firefox will create a new, clean profile on the next startup. If this does not solve the problem the changes can be easily reverted. It is necessary to close all instances of Firefox before proceeding:
user $cd ~/.mozilla
user $rm -r firefox
user $mv firefox_bak firefox
If this solves the issue and profile related settings are required, a breakdown of the related files with their purpose can be found in this Mozilla guide.
In this case make sure, to backup the whole profile folder first, before merging the old files with the new once.
Firefox forked projects
- GNU Icecat — a web browser developed by the GNU project that is entirely Free Software
- LibreWolf — a fork of Firefox which focuses on privacy and security.
- Pale Moon — Pale Moon Web Browser.
See also
- Thunderbird — Mozilla's solution to the e-mail client.
External resources
- The official Firefox wiki (out-of-date)
- Firefox on Mozilla's Forums
- Firefox on Mozilla's Buglist
- Change the interface language (L10N)
- Creating a new profile
- Firefox about:config privacy enhancements
References
- ↑ https://askubuntu.com/a/95333
- ↑ https://www.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/66.0/releasenotes
- ↑ https://bugzilla.mozilla.org/show_bug.cgi?id=1732358
- ↑ https://bugzilla.mozilla.org/show_bug.cgi?id=1742892#c0
- ↑ https://firefox-source-docs.mozilla.org/dom/ipc/process_model.html#isolated-web-content
- ↑ https://github.com/mozilla/cubeb/wiki/Backend-Support
- ↑ https://github.com/mozilla/cubeb/blob/master/src/cubeb.c#L150
- ↑ https://support.mozilla.org/en-US/kb/privacy-preserving-attribution
- ↑ https://blog.mozilla.org/netpolicy/2024/08/22/ppa-update/
- ↑ https://lunduke.locals.com/post/5871895/mozilla-firefox-goes-anti-privacy-pro-advertising
- ↑ https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=40974112
- ↑ https://www.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/130.0/releasenotes/
- ↑ https://support.mozilla.org/en-US/kb/ai-chatbot
- ↑ https://connect.mozilla.org/t5/discussions/ai-chatbot-at-your-service/td-p/84919
- ↑ https://addons.mozilla.org/en-GB/firefox/addon/ublock-origin/
- ↑ https://adnauseam.io/
- ↑ https://www.technologyreview.com/2021/01/06/1015784/adsense-google-surveillance-adnauseam-obfuscation/
- ↑ https://support.mozilla.org/en-US/kb/customizing-firefox-using-policiesjson
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File_URI_scheme
- ↑ https://support.mozilla.org/en-US/kb/speechd-setup
- ↑ https://forums.gentoo.org/viewtopic-t-1160601-highlight-gdkwarning.html
- ↑ https://support.mozilla.org/en-US/kb/diagnose-firefox-issues-using-troubleshoot-mode#w_what-does-troubleshoot-mode-disable
- ↑ https://support.mozilla.org/en-US/kb/diagnose-firefox-issues-using-troubleshoot-mode#w_how-to-start-firefox-in-troubleshoot-mode
- ↑ https://support.mozilla.org/en-US/kb/refresh-firefox-reset-add-ons-and-settings?redirectslug=reset-firefox-easily-fix-most-problems&redirectlocale=en-US#w_these-items-and-settings-will-be-removed
- ↑ https://support.mozilla.org/en-US/kb/refresh-firefox-reset-add-ons-and-settings?redirectslug=reset-firefox-easily-fix-most-problems&redirectlocale=en-US#w_firefox-will-save-these-items